作者:聂勇 欢迎转载,请保留作者信息并说明文章来源!
JDK提供了非常多的集合类,不仅使用简单,而且功能丰富,可以满足你绝大部分的需求。但在使用的时候如果不了解其实现的原理,有可能会碰到性能方面的问题,或者在一起场景下会导致系统故障。
前段时间Review代码,发现有同学在使用HashMap时存在一些问题:
1、在并发场景下使用HashMap。
2、数据量较大时,使用默认的容量。
下面主要讲解HashMap的存储结构、查询数据和插入数据的实现。
数据存储结构
采用双表结构:数组+单向链表。
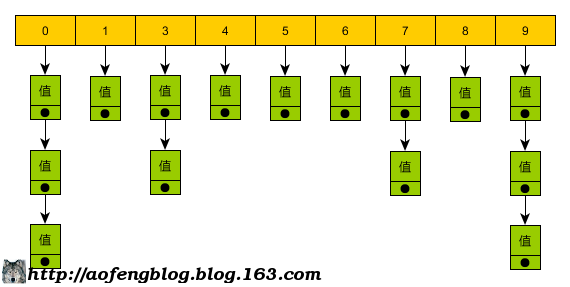
代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| transient Entry[] table; Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; }
|
插入数据(put方法)
put方法的代码非常清晰简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
| public V put(K key, V value) { if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
|
生成单向链表
再来看看新增数据时(addEntry方法)是如何实现的:
PS:新增的数据始终位于链表的头部。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); if (size++ >= threshold) resize(2 * table.length); }
|
扩容
1、在插入数据时,如果存储的数据量大于或等于阈值(threshold)时,就会执行扩容(resize)操作。
- 阈值=容量 x 阈值系数。
- 容量默认值为16。
- 阈值系数默认值为0.75。
2、如何扩容:按新容量创建一个数据,将旧数据中的无素一个一个地重新计算索引位置并写入(见transfer方法)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
| void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable); table = newTable; threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); } void transfer(Entry[] newTable) { Entry[] src = table; int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; if (e != null) { src[j] = null; do { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } while (e != null); } } }
|
获取数据(get方法)
get方法比put方法的代码更简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
| public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) return getForNullKey(); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) return e.value; } return null; }
|
注意事项
1、如果可以预估数据量,在创建HashMap实例时,设置合适的初始容量,可以减少扩容操作,提升性能。
2、将容量设置为2的n次方性能最好,如:16,32。原因:和HashMap的indexFor方法实现有关。
3、用作Key的对象须实现equals和hashCode方法。如果用String对象作Key,就不用自己实现equals和hashCode方法,因为String对象已经实现。
4、HashMap是非线程安全的,在多线程并发操作时会出现死循环。原因:执行扩容操作时,将旧表中的数据插入新表时有可能导致单向链表形成闭环。
